Understanding Water Electrolysers: The Future of Clean Energy | Hydrogen Production Technology

In the quest for sustainable energy solutions, water electrolysers have emerged as a pivotal technology. These devices, which use electricity to split water into hydrogen and oxygen, are at the forefront of producing clean hydrogen fuel. As the world shifts towards renewable energy sources, understanding the role and potential of water electrolysers becomes essential. This article delves into the intricacies of water electrolysers, exploring their types, applications, and future in the energy landscape.
What Are Water Electrolysers?
Water electrolysers are devices that facilitate the process of water electrolysis, splitting water molecules (H₂O) into hydrogen (H₂) and oxygen (O₂) using electricity. This process is crucial for producing hydrogen, a clean and energy-dense fuel, from water, an abundant resource. The hydrogen produced can be used in various applications, from powering fuel cells in vehicles to serving as a feedstock in industrial processes.
Types of Water Electrolysers
There are three primary types of water electrolysers, each with unique characteristics and applications:
- Alkaline Electrolysers: These use a liquid electrolyte solution, such as potassium hydroxide (KOH), to conduct electricity. Alkaline electrolysers are a mature technology, known for their reliability and cost-effectiveness. They are widely used in industrial applications but are bulkier compared to other types.
- Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM) Electrolysers: PEM electrolysers use a solid polymer electrolyte to conduct protons from the anode to the cathode. They are compact and efficient, making them suitable for applications requiring flexibility and rapid response to changes in power supply, such as renewable energy integration.
- Solid Oxide Electrolysers (SOEC): Operating at high temperatures, SOECs use a solid ceramic electrolyte. They offer high efficiency and can produce both hydrogen and oxygen in a single device. However, they are still in the development phase and not yet widely commercialized.
How Do Water Electrolysers Work?
The basic mechanism of water electrolysis involves two electrodes: an anode and a cathode. When electricity is applied, water molecules at the anode split into oxygen, protons, and electrons. The electrons flow through an external circuit, while the protons move across the electrolyte to the cathode, where they combine with electrons to form hydrogen gas.
Reactions in Water Electrolysis
- Anode Reaction: (2H_2O \rightarrow O_2 + 4H^+ + 4e^-)
- Cathode Reaction: (4H^+ + 4e^- \rightarrow 2H_2)
- Total Reaction: (2H_2O \rightarrow O_2 + 2H_2)

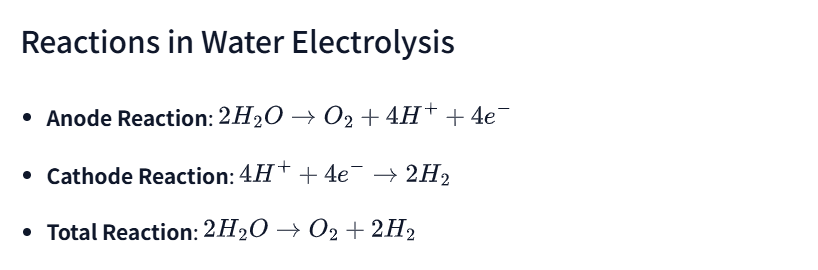
Applications of Water Electrolysers
Water electrolysers have a wide range of applications across various sectors:
- Power to Mobility: Hydrogen produced can be used as fuel for fuel-cell electric vehicles (FCEVs), such as buses, trains, and cars, providing a clean alternative to fossil fuels.
- Power to Industry: Electrolysers can produce hydrogen for industrial processes, such as steel manufacturing and semiconductor production, reducing carbon emissions.
- Power to Gas: Hydrogen can be injected into natural gas grids, lowering carbon intensity, or used to produce green chemicals like methanol and ammonia.
- Energy Storage: Electrolysers can convert excess renewable energy into hydrogen, which can be stored and later converted back to electricity using fuel cells, stabilizing the grid.
The Role of Water Electrolysers in Clean Energy Transitions
In the transition to a net-zero emissions future, water electrolysers play a crucial role. They enable the production of low-emission hydrogen from renewable or nuclear electricity, providing a sustainable energy solution for hard-to-decarbonize sectors like heavy industry and long-distance transport.
Current Trends and Future Outlook
Electrolysis capacity for dedicated hydrogen production is growing, with significant investments and policy support driving this expansion. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), global electrolyser capacity could reach up to 365 GW by 2030, a substantial increase from current levels.
Countries like China, the European Union, and the United States are leading the charge, with ambitious plans to scale up electrolyser deployment. These efforts are crucial to meet the targets set under the Net Zero Emissions by 2050 scenario, which requires more than 550 GW of electrolysers globally by the end of the decade.
Challenges and Innovations
Despite the promising potential of water electrolysers, several challenges remain. The high cost of electrolysers, particularly PEM and SOEC technologies, is a significant barrier to widespread adoption. However, ongoing research and development efforts aim to reduce costs through economies of scale and technological advancements.
Innovations in critical materials intensity reduction and system efficiency are also progressing. For example, new designs like membrane-free electrolysers and catalyst-coated membranes with reduced precious metal content are emerging, promising to lower costs and improve performance.
Conclusion
Water electrolysers are a cornerstone of the clean energy transition, offering a sustainable solution for hydrogen production. As technology advances and costs decrease, their role in decarbonizing various sectors will only grow. Policymakers and industry leaders must continue to support the development and deployment of electrolysers to realize their full potential in achieving a sustainable energy future.
Call to Action
To stay informed about the latest developments in water electrolysers and clean energy technologies, consider subscribing to industry newsletters, participating in webinars, and engaging with professional networks. Your involvement can help drive the innovation and adoption of these critical technologies, contributing to a cleaner, more sustainable world.







