I. Introduction: The Dawn of Green Hydrogen and PEM’s Leading Role
A. The Global Imperative for Decarbonization and Green Hydrogen
The world stands at a pivotal juncture, grappling with the urgent need to decarbonize its energy systems and industrial processes. Amidst this global challenge, hydrogen has emerged as a truly transformative energy carrier, holding the key to unlocking a sustainable future. Unlike traditional fossil fuels, hydrogen—especially green hydrogen—offers a versatile, clean solution for energy storage, transportation, and industrial feedstock.
The demand for low-carbon hydrogen is not merely a projection; it’s a rapidly accelerating reality. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), the global demand for hydrogen could reach 200 million metric tons annually by 2050, up from around 90 Mt today, driven largely by new applications in heavy industry, shipping, and aviation. This monumental shift necessitates robust, efficient, and scalable production technologies. It’s here that proton exchange membrane electrolysis systems (PEM electrolyzers) are not just participating but leading the charge, redefining what’s possible in hydrogen production technology.
Green hydrogen, produced through water electrolysis powered by renewable electricity, is the cornerstone of this transition. It offers a pathway to significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions, enabling industries to move away from carbon-intensive processes.
The market value of this burgeoning sector is staggering, with forecasts predicting multi-trillion-dollar valuations in the coming decades, creating unprecedented opportunities for early adopters and technology providers alike.

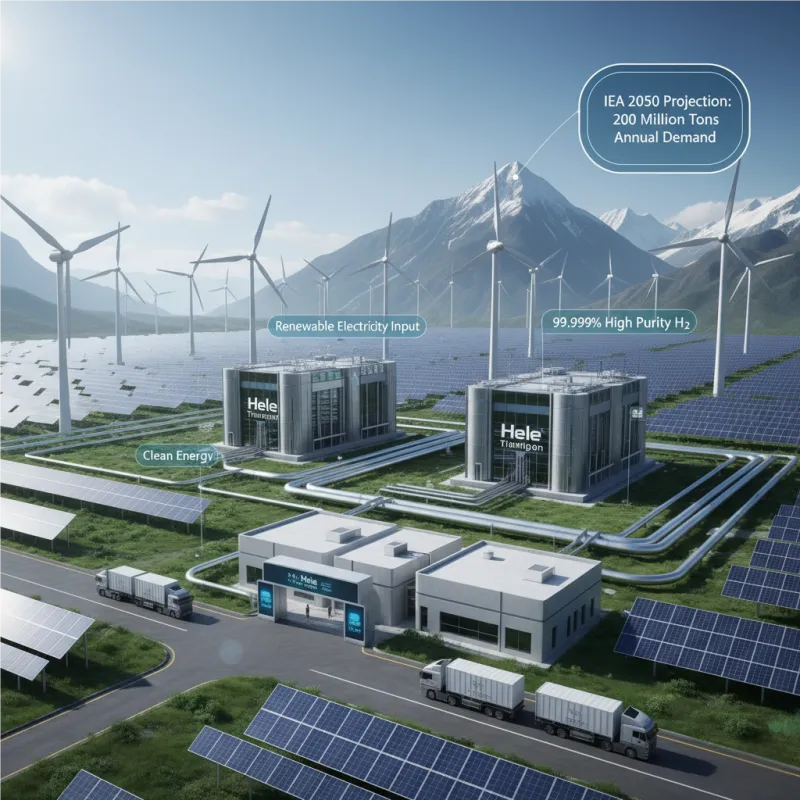
Image 1: Large-scale Green Hydrogen Production Facility Integrating Solar, Wind, and PEM Electrolyzers (Caption: A visionary depiction of a green hydrogen production complex, where solar panels and wind turbines power advanced PEM electrolysis systems. This facility efficiently converts water into ultra-high-purity hydrogen, ready for industrial use or energy storage. Such systems are crucial to meet the projected 200 million tons annual demand for low-carbon hydrogen by 2050, demonstrating the immense potential of PEM technology in the global energy transition. Courtesy of Hele Titanium Hydrogen.)
B. Why PEM Electrolysis is the Next-Generation Solution for Industrial Hydrogen
For decades, alkaline electrolysis has been the workhorse of industrial hydrogen production. However, the unique demands of the renewable energy era—namely, fluctuating power sources and the need for compact, highly responsive systems—have propelled PEM technology to the forefront. PEM electrolyzers offer a suite of advantages that position them as the premier choice for next-generation hydrogen production technology:
- Unmatched Efficiency: Optimizing energy conversion for reduced operational costs.
- Dynamic Operation: Rapid response capabilities perfectly align with intermittent renewable energy sources like solar and wind.
- High-Purity Output: Producing hydrogen that meets the most stringent industrial specifications without extensive post-processing.
- Compact Footprint: Enabling flexible deployment in various settings.
This article serves as a comprehensive guide for commercial decision-makers, offering deep insights into the technology, operational benefits, economic considerations, and diverse applications of PEM electrolysis systems. We aim to equip you with the knowledge to make informed strategic investments in this critical area.
C. Hele Titanium Hydrogen: Your Partner in Advanced PEM Technology
At Hele Titanium Hydrogen, we are not just observers of this energy revolution; we are active participants and innovators. As a professional manufacturer and wholesale supplier of high-performance PEM water hydrogen generators, we specialize in the design, development, and manufacturing of custom OEM & Manufacturing services. Our commitment to precision engineering and quality makes us an ideal partner for businesses looking to integrate state-of-the-art PEM electrolysis into their operations. Our experience in foreign trade B2B ensures seamless collaboration and delivery for international clients.
II. Deeper Dive: How Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM) Electrolysis Systems Work
Understanding the fundamental science behind PEM electrolysis is crucial for appreciating its capabilities. This technology elegantly leverages electrochemistry to split water molecules, yielding high-purity hydrogen and oxygen.
A. The Fundamental Electrochemistry: Splitting Water for Hydrogen
The core principle of water electrolysis is straightforward: applying an electrical current to water (H₂O) to break it down into its constituent elements—hydrogen (H₂) and oxygen (O₂). In a PEM electrolyzer, this process occurs in two distinct half-reactions:
- At the Anode (Positive Electrode): Water molecules are oxidized, releasing oxygen gas, protons (H⁺ ions), and electrons (e⁻).
2H₂O(l) → O₂(g) + 4H⁺(aq) + 4e⁻
- At the Cathode (Negative Electrode): Protons, having traveled across the membrane, combine with electrons from the external circuit to form hydrogen gas.
4H⁺(aq) + 4e⁻ → 2H₂(g)
The overall reaction is: 2H₂O(l) + Electrical Energy → 2H₂(g) + O₂(g)
This elegant electrochemical process ensures that the hydrogen produced is separated from the oxygen, with the crucial role played by the proton exchange membrane.
It’s imperative that the water feed is deionized (ultra-pure) to prevent catalyst poisoning and membrane degradation, extending the system’s longevity and maintaining peak performance.
B. Anatomy of a High-Performance PEM Electrolyzer Cell
A single PEM electrolyzer cell is a marvel of material science and engineering. Multiple cells are typically stacked together to form an electrolyzer stack, allowing for scaled-up hydrogen production.
1. The Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM): The Heart of the System
The proton exchange membrane is the defining component of PEM technology. Typically made from a perfluorosulfonic acid polymer (like Nafion), this thin, solid membrane performs two critical functions:
- Proton Conduction: It efficiently conducts positively charged protons (H⁺ ions) from the anode to the cathode.
- Gas Barrier: Crucially, it acts as an impermeable barrier to electron flow and prevents the mixing of hydrogen and oxygen gases, ensuring high product purity and safety.
At Hele Titanium Hydrogen, we meticulously select membrane materials for their superior ion conductivity, thermal stability, and mechanical strength, guaranteeing the durability and high performance of our PEM cells.
2. Catalyst-Coated Electrodes: Driving the Reaction
High-performance electrodes are essential for accelerating the electrochemical reactions.
- Anode Catalyst: Usually iridium oxide (IrO₂) or ruthenium oxide (RuO₂), which are highly active for the oxygen evolution reaction.
- Cathode Catalyst: Typically platinum (Pt), which is excellent for the hydrogen evolution reaction.
These platinum group metals (PGMs) are deposited onto porous electrode backings to maximize surface area and catalytic activity. While effective, the cost of PGMs is a significant driver of PEM electrolysis cost, spurring intensive research into reducing their loading or finding more abundant alternatives.
3. Bipolar Plates & Flow Fields: Precision and Distribution
Between each cell in a stack are bipolar plates. These plates:
- Conduct Electricity: Electronically connect cells in series.
- Distribute Reactants/Products: Feature intricate flow fields (channels) to efficiently deliver water to the electrodes and remove the generated hydrogen and oxygen gases.
- Mechanical Support: Provide structural integrity to the stack.
High-quality materials like titanium, often with specialized coatings, are used for bipolar plates due to their excellent corrosion resistance in the highly acidic PEM environment.
4. Balance of Plant (BOP): The Supporting Infrastructure
The electrolyzer stack is the core, but a sophisticated Balance of Plant (BOP) is necessary for a complete, operational PEM electrolysis system. Key BOP components include:
- DC Power Supply/Rectifier: Converts AC grid power to the DC current required for electrolysis.
- Water Purification System: Deionizes feed water to protect the membrane and catalysts.
- Gas Separation and Drying Units: Separates hydrogen and oxygen, removes residual water vapor.
- Hydrogen Compression & Storage: Compresses the produced hydrogen to required pressures for storage or direct use.
- Thermal Management System: Controls the operating temperature of the electrolyzer stack for optimal efficiency and longevity.
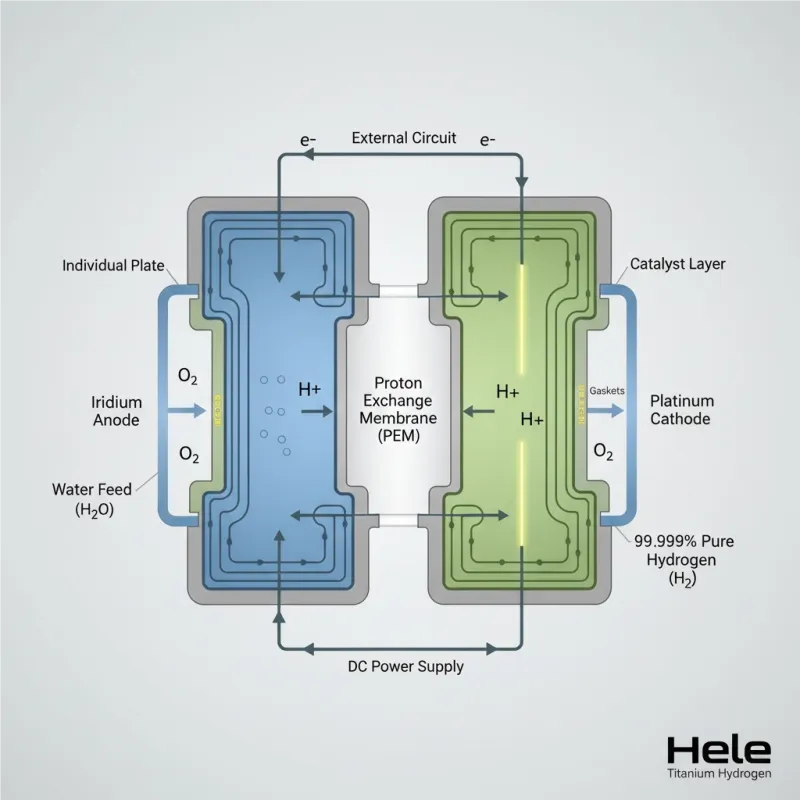
Image 2: Detailed Diagram of a Single PEM Electrolyzer Cell (Caption: A simplified cross-section illustrating the core functionality of a PEM electrolyzer cell. Deionized water enters, and under the influence of electric current, splits at the anode (right), releasing oxygen, protons, and electrons. Protons traverse the proton exchange membrane, while electrons flow through an external circuit. At the cathode (left), protons and electrons recombine to form 99.999% pure hydrogen. This fundamental process underpins the efficiency of PEM electrolysis systems. Courtesy of Hele Titanium Hydrogen.)
III. Unpacking the Advantages: Why PEM Systems Excel for Commercial Applications
The distinct advantages of PEM electrolysis systems go beyond mere technical specifications; they translate directly into tangible commercial benefits, making them the preferred choice for forward-thinking industries.
A. Unmatched Efficiency and Hydrogen Purity
1. High Current Density Operation: Compact Powerhouses
One of the standout features of PEM technology is its ability to operate at high current densities—typically ranging from 1 to 3 A/cm², and even higher in advanced systems. This means a significant amount of hydrogen can be produced from a relatively small electrode area. The direct commercial implications are profound:
- Compact Footprint: High current density leads to smaller, more compact electrolyzer stacks, reducing the physical space required for installation. This is critical for urban environments, existing industrial sites with limited space, or modular deployments.
- Higher Production Rates: More hydrogen produced per unit of equipment, optimizing capital expenditure efficiency.
2. Superior Hydrogen Purity (Up to 99.999%): Eliminating Extra Steps
PEM electrolyzers inherently produce hydrogen of exceptionally high purity, often reaching 99.999% or even higher, directly from the stack. This is primarily due to the solid, impermeable nature of the proton exchange membrane, which effectively prevents the crossover of hydrogen and oxygen gases.
- Cost Savings: This high purity often eliminates or significantly reduces the need for expensive and energy-intensive downstream purification processes, translating into direct cost of hydrogen reductions for end-users.
- Application Suitability: Such ultra-high purity hydrogen is essential for sensitive applications like fuel cells, semiconductor manufacturing, and specialized chemical processes, where even trace impurities can be detrimental.
3. Energy Efficiency Metrics: Optimizing Operational Costs
The overall energy efficiency of a PEM electrolysis system is a critical factor influencing its operational expenditure (OPEX). Modern PEM electrolyzers typically achieve energy efficiencies in the range of 60-70% (based on the Higher Heating Value, HHV), with advanced systems pushing towards 75% and beyond.
- Cell Voltage: The lower the cell voltage required to drive the reaction, the higher the electrical efficiency.
- Stack Efficiency: Reflects the performance of the electrolyzer stack itself.
- System Efficiency: Accounts for the energy consumption of the entire Balance of Plant (BOP) components.
By minimizing energy input per kilogram of hydrogen produced, PEM technology directly contributes to a lower Levelized Cost of Hydrogen (LCOH).
B. Dynamic Responsiveness: Ideal for Renewable Energy Integration
The intermittent nature of renewable energy sources like solar and wind power presents a significant challenge for grid stability. PEM electrolysis is uniquely positioned to solve this, offering unparalleled dynamic responsiveness.
1. Fast Start-up and Shut-down Times: Seizing Every Electron
Unlike traditional alkaline electrolyzers, which can take hours to ramp up or down, PEM systems can go from standby to full power in mere seconds to minutes. This rapid response capability is a game-changer for:
- Capturing Transient Energy: Maximizing the utilization of surplus renewable electricity when it’s cheapest or most abundant.
- Grid Balancing: Providing valuable grid services by quickly adjusting hydrogen production to match grid demands or renewable fluctuations, turning an operational challenge into an asset.
2. Broad Operating Range: Flexibility in Power Input
PEM electrolyzers can operate efficiently across a wide turndown ratio, typically from 5% to 100% of their nominal capacity. This broad operating range allows them to:
- Seamlessly Integrate with Renewables: Efficiently manage the variability inherent in wind and solar generation, producing green hydrogen whenever renewable power is available.
- Problem Solved: This feature directly addresses the issue of renewable energy curtailment, turning otherwise wasted electricity into a valuable, storable energy carrier.
C. Compact Design and Scalable Modular Architecture
The high current density of PEM technology allows for a significantly smaller equipment footprint compared to other electrolysis methods.
- Reduced Space Requirements: This is a major advantage for installations in constrained urban or industrial areas.
- Modular Design: PEM electrolyzers are inherently modular, meaning multiple stacks can be combined to achieve desired production capacities. This offers:
- Easy Expansion: Systems can be scaled up incrementally as demand grows.
- Custom System Sizing: Tailoring solutions precisely to client needs, from small on-site generators to multi-megawatt industrial plants.
- Easy Expansion: Systems can be scaled up incrementally as demand grows.
Hele’s Edge: At Hele Titanium Hydrogen, our design philosophy prioritizes modularity and compactness. We excel in designing and manufacturing compact, scalable OEM hydrogen generators that integrate seamlessly into existing infrastructure or greenfield projects, offering unparalleled flexibility to our clients.
D. Enhanced Safety and Operational Simplicity
Safety is paramount in any industrial operation, especially when dealing with hydrogen. PEM electrolysis offers inherent safety advantages:
1. Solid Electrolyte Advantage: No Corrosive Liquids
The use of a solid proton exchange membrane eliminates the need for handling highly corrosive liquid electrolytes (like potassium hydroxide in alkaline systems). This significantly:
- Reduces Chemical Handling Risks: Minimizing hazards for operational personnel.
- Simplifies Maintenance Procedures: Less complex safety protocols compared to managing corrosive fluids.
- Environmental Benefit: Eliminates the risk of hazardous electrolyte spills.
2. Minimal Differential Pressure Operation: Preventing Gas Mixing
The robust design of PEM cells, combined with the membrane’s gas impermeability, helps maintain minimal differential pressure between the hydrogen and oxygen streams, further reducing the risk of gas mixing—a critical safety concern in electrolysis.
3. Lower Maintenance Requirements: Optimized Uptime
With fewer moving parts and a robust, sealed design, PEM electrolysis systems typically demand less frequent maintenance compared to older technologies. This translates to:
- Reduced Operational Burden: Lower labor costs for maintenance.
- Increased System Uptime: Maximizing hydrogen production and revenue generation.
E. Long-Term Reliability and Durability
While the use of PGMs might seem a disadvantage in terms of initial cost, it contributes to the long-term stability and durability of the catalysts under the acidic PEM operating conditions.
- Extended System Lifespan: Modern PEM electrolyzers are designed for lifespans of 60,000 to 80,000 operating hours for the stack, with ongoing research pushing towards 100,000 hours, equating to over 10 years of continuous operation.
- Robustness: PEM systems demonstrate remarkable resilience to rapid load changes, which is crucial for renewable energy integration, ensuring consistent performance over many operational cycles.
Hele’s Edge: At Hele Titanium Hydrogen, our unwavering commitment to using premium-grade materials and implementing stringent manufacturing quality controls directly translates into PEM water hydrogen generators that deliver exceptional long-term reliability and performance, providing our clients with peace of mind and optimized returns on investment.
IV. Performance Metrics and Cost Analysis: Making an Informed Investment
For any industrial client, the decision to invest in PEM electrolysis systems hinges on a thorough understanding of performance capabilities and economic viability. This section delves into the critical metrics that matter.
A. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for PEM Electrolysis
When evaluating electrolysis systems, specific KPIs provide a clear picture of their operational effectiveness:
1. Hydrogen Production Rate
Measured in Normal cubic meters per hour (Nm³/hr) or kilograms per day (kg/day), this indicates the system’s output capacity. It’s directly proportional to the current density and the number of active cells in the stack. Larger industrial applications will require systems capable of hundreds or thousands of Nm³/hr.
2. Energy Consumption (kWh/Nm³ H₂ or kWh/kg H₂)
This is perhaps the most critical OPEX driver. It measures the electrical energy required to produce a specific amount of hydrogen. Current commercial PEM electrolyzers typically consume between 45-55 kWh/kg H₂ (equivalent to 4.0-4.9 kWh/Nm³ H₂), with continuous efforts to reduce this figure. A lower kWh/kg H₂ translates directly to lower operating costs, especially when electricity prices are volatile.
3. Hydrogen Purity
As discussed, PEM systems deliver up to 99.999% purity, a key differentiator. Verifying this purity with supplier specifications and independent certifications is vital, particularly for applications like fuel cells and electronics.
4. System Availability/Uptime
Expressed as a percentage, this metric indicates how often the system is operational and producing hydrogen. High availability (e.g., >95%) is essential for continuous industrial processes and maximizing return on investment.
5. Degradation Rate
Over time, the performance of electrolyzer components (catalysts, membrane) can subtly degrade, leading to a slight increase in energy consumption for the same hydrogen output. A low degradation rate (e.g., < 10 µV/hr per cell) indicates a well-designed and durable system, critical for long-term predictability of OPEX.
B. Decoding the Economics: CAPEX, OPEX, and LCOH
The true cost-effectiveness of PEM electrolysis is determined by a holistic view of both initial investment and ongoing operational expenses, culminating in the Levelized Cost of Hydrogen (LCOH).
1. Capital Expenditure (CAPEX) Breakdown
The initial investment for a PEM electrolysis system comprises several key components:
- Electrolyzer Stack: This is often the largest cost driver, accounting for 40-50% of the total CAPEX. It includes the cost of the proton exchange membrane, the expensive platinum group metal (PGM) catalysts, and the titanium bipolar plates.
- Balance of Plant (BOP): Typically 30-40% of CAPEX, this includes the power rectifier, water purification system, gas handling, hydrogen compression, cooling systems, and control units. The BOP is crucial for integrating the stack into a complete, safe, and efficient system.
- Installation and Project Management: The remaining 10-20% covers civil works, piping, electrical connections, engineering, and commissioning.
Trend Analysis: While traditionally higher than alkaline systems, PEM electrolyzer costs have seen a significant reduction in recent years. Analysts project a further 30-50% reduction in CAPEX by 2030 due to economies of scale in manufacturing, technological advancements in material science (e.g., lower PGM loading), and streamlined production processes.
2. Operational Expenditure (OPEX) Factors
Ongoing costs are crucial for long-term viability:
- Electricity Costs (The Largest Component): This typically accounts for 70-80% of the total OPEX for green hydrogen production. The price and availability of renewable energy (e.g., through Power Purchase Agreements – PPAs) are paramount. A lower, stable electricity price is the single most impactful factor in reducing cost of hydrogen.
- Water Consumption and Treatment: While relatively small, the cost of deionized water and the energy for its purification is a recurring expense.
- Maintenance and Spares: Includes routine checks, component replacements (e.g., filters, occasional membrane refurbishment), and labor. Modern PEM systems are designed for minimal maintenance, but planning for periodic servicing is essential.
- Labor Costs: For operation and supervision.
3. Levelized Cost of Hydrogen (LCOH): Your Ultimate Economic Metric
The Levelized Cost of Hydrogen (LCOH) is the most comprehensive metric for evaluating the economic viability of a hydrogen production project. It represents the average cost per kilogram of hydrogen produced over the system’s lifetime, factoring in all CAPEX, OPEX, financing, and a discount rate.
- Current LCOH: For new PEM projects utilizing dedicated renewable energy, current LCOH typically ranges from $4-6 per kg H₂, heavily dependent on local electricity prices and CAPEX.
- Future Projections: With declining renewable energy costs, falling electrolyzer CAPEX, and improved efficiencies, the LCOH for green hydrogen from PEM is projected to fall below $2 per kg H₂ by 2035, making it competitive with, and eventually cheaper than, grey hydrogen.
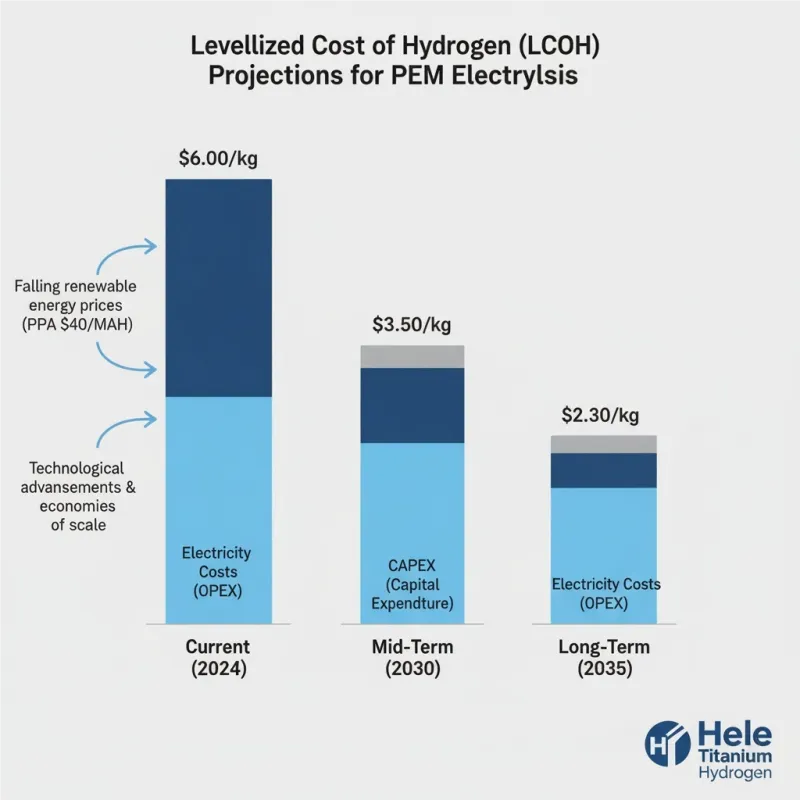
Image 3: Levelized Cost of Hydrogen (LCOH) Breakdown & Projections for PEM Electrolysis (Caption: This infographic illustrates the current and projected Levelized Cost of Hydrogen (LCOH) for PEM electrolysis systems. It highlights how a significant reduction in CAPEX and OPEX—primarily driven by falling renewable energy prices (e.g., from $40/MWh) and technological advancements—is poised to lower LCOH from current levels of around $6.00/kg to below $2.00/kg by 2035. This makes green hydrogen increasingly competitive with traditional fossil-fuel-based production.
Courtesy of Hele Titanium Hydrogen.)
4. Cost Reduction Strategies and ROI Optimization
Achieving a competitive LCOH requires strategic planning and leveraging several key drivers:
- Economies of Scale: Increased production volumes of electrolyzers drive down manufacturing costs.
- Technological Advancements: Continuous R&D in catalysts (reducing PGM loading), membranes, and system design improves efficiency and durability.
- Optimized System Integration: Efficient pairing of electrolyzers with renewable energy sources minimizes electricity losses and maximizes utilization.
- Policy Support: Government incentives, subsidies, carbon pricing mechanisms, and tax credits significantly de-risk projects and improve financial viability.
Call to Action: Curious about the potential ROI for your specific industrial application? Contact Hele Titanium Hydrogen today for a tailored cost-benefit analysis and explore how our OEM hydrogen generator solutions can optimize your green hydrogen production.
V. Diverse Industrial Applications of PEM Electrolysis Systems
The versatility and efficiency of PEM electrolysis technology make it suitable for a vast array of industrial and energy-related applications, driving decarbonization across multiple sectors.
A. Decarbonizing Heavy Industry: Ammonia, Steel, and Chemicals
Heavy industries, historically major emitters, are prime candidates for green hydrogen integration.
1. Green Ammonia Production
Hydrogen is a primary feedstock for ammonia (NH₃) synthesis (Haber-Bosch process). Producing ammonia from green hydrogen (instead of hydrogen derived from natural gas) leads to green ammonia, a crucial component for fertilizers and a promising carbon-free marine fuel. * Proof Point: Large-scale projects, such as the NEOM project in Saudi Arabia, plan to produce green ammonia using gigawatts of PEM electrolysis powered by solar and wind.
2. Green Steel Production
The steel industry accounts for 7-9% of global CO₂ emissions. Green hydrogen can replace metallurgical coal as a reductant in the direct reduced iron (DRI) process, leading to green steel production with significantly lower emissions. * Case Study Example: H2 Green Steel’s Boden project in Sweden aims to produce fossil-free steel by 2025, relying heavily on PEM electrolysis for its hydrogen supply.
3. Chemical Feedstock
Beyond ammonia, hydrogen is vital for numerous chemical processes, including methanol synthesis, hydrogenation reactions, and the production of various industrial chemicals. Using green hydrogen directly impacts the sustainability profile of the entire chemical supply chain.
B. Power-to-X and Energy Storage: Bridging Energy Gaps
PEM electrolysis is a critical enabler of the Power-to-X concept, converting excess renewable energy into valuable products or storable forms.
1. Grid-Scale Energy Storage
When wind farms generate more electricity than the grid can consume, or solar power peaks during the day, PEM electrolyzers can convert this surplus electricity into green hydrogen. This hydrogen can be stored and later used to generate electricity (via fuel cells or turbines) during periods of high demand or low renewable output, effectively functioning as a large-scale energy battery.
2. Power-to-Gas (P2G)
P2G involves converting electricity into hydrogen, which can then be directly injected into existing natural gas pipelines (up to a certain blending limit) or further processed into synthetic methane. This leverages existing infrastructure for energy storage and distribution.
3. Power-to-Liquid (P2L)
By combining green hydrogen with captured CO₂, PEM electrolysis facilitates the creation of synthetic fuels (e-fuels) like sustainable aviation fuel (SAF), e-diesel, or e-kerosene. These P2L fuels are vital for decarbonizing hard-to-electrify sectors like aviation and heavy shipping.
Case Study Example: The Haru Oni project in Chile uses wind power, PEM electrolysis, and captured CO₂ to produce e-methanol and e-gasoline, demonstrating a full Power-to-Liquid value chain.
C. Fuel Cell Vehicles (FCVs) and Sustainable Mobility
The transportation sector is another key area for hydrogen production.
1. Passenger Cars and Heavy-Duty Transport
Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles (FCVs) offer zero tailpipe emissions, fast refueling, and long ranges, making them attractive alternatives to traditional combustion engine vehicles, particularly for heavy-duty trucks, buses, and trains. The ultra-high purity hydrogen from PEM systems is ideally suited for sensitive fuel cells.
2. Hydrogen Refueling Infrastructure
PEM electrolyzers play a crucial role in building out hydrogen refueling station networks. They can provide on-site, decentralized hydrogen production, reducing the need for costly and energy-intensive hydrogen transportation. This localized production model enhances the economic viability and reliability of refueling stations.
Hele’s Relevance: Our compact and efficient PEM water hydrogen generators are perfectly suited for integration into refueling stations, offering reliable and cost-effective hydrogen generation at the point of demand, thereby accelerating the adoption of FCVs.
D. Emerging and Niche Applications
Beyond these major sectors, PEM technology is finding its way into specialized niches:
1. Electronics and Semiconductor Manufacturing
The electronics industry demands incredibly high-purity hydrogen for various manufacturing steps (e.g., as a reducing agent, carrier gas, or for annealing processes). PEM electrolysis is a natural fit, providing the required 99.999% purity without compromise.
2. Glass Manufacturing
Hydrogen can serve as a clean fuel in glass furnaces, helping to reduce the industry’s carbon footprint.
3. Microgrids and Remote Power Solutions
For off-grid communities, islands, or critical infrastructure, PEM electrolysis can integrate with local renewables to produce hydrogen for energy storage, ensuring reliable, uninterrupted power supply.
Case Study Example: The Orkney Islands in Scotland have pioneered a “hydrogen economy” using local wind and tidal power to fuel PEM electrolyzers, supporting local transport, heat, and grid balancing.
E. Hele Titanium Hydrogen in Action: Our Contributions to Diverse Sectors
At Hele Titanium Hydrogen, our OEM & Manufacturing services extend across many of these critical sectors. We have partnered with clients to develop:
- Compact PEM hydrogen generators for integration into renewable energy demonstration projects.
- Scalable electrolysis systems for pilot green ammonia plants.
- Specialized high-purity hydrogen solutions for electronics manufacturing partners.
Our hands-on experience in these varied applications reinforces our expertise and ability to deliver bespoke PEM technology solutions that meet stringent industry demands.
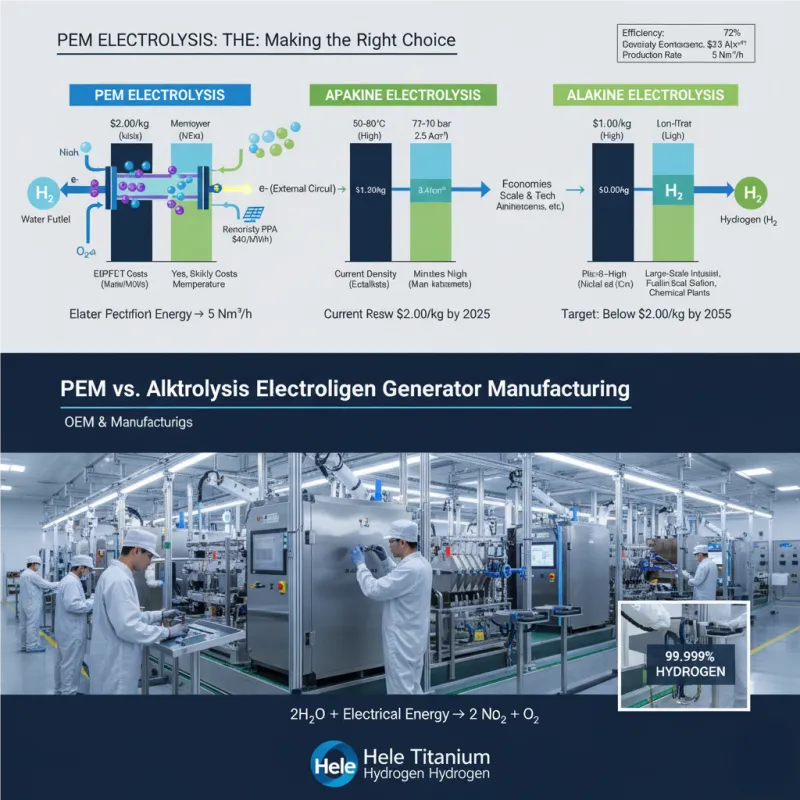
VI. PEM Electrolysis vs. Alkaline Electrolysis: Choosing the Right Technology
While both PEM and alkaline electrolysis split water to produce hydrogen, their fundamental differences make them suitable for distinct applications and operational environments. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for selecting the optimal electrolysis system for your project.
A. Technological Fundamentals: Key Distinctions
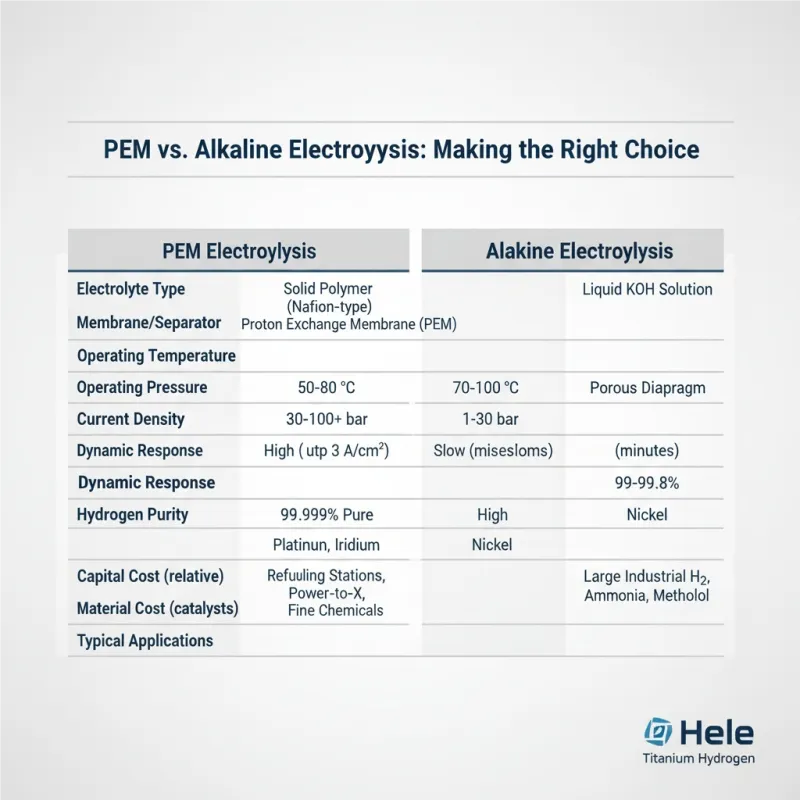
| Feature | PEM Electrolysis | Alkaline Electrolysis |
|---|---|---|
| Electrolyte Type | Solid polymer membrane (e.g., Nafion) | Liquid alkaline solution (e.g., KOH, NaOH) |
| Operating Temperature | 50-80°C (medium temperature) | 70-100°C (medium to high temperature) |
| Operating Pressure | Up to 30-70 bar (can integrate compression) | 10-30 bar (typically lower pressure output) |
| Current Density | 1-3 A/cm² (high) | 0.2-0.4 A/cm² (lower) |
| Catalysts | Platinum (cathode), Iridium/Ruthenium (anode) | Nickel-based materials (non-PGM) |
| Gas Separation | Direct, membrane-based (high purity) | Requires gas separators and purifiers (lower purity) |
B. Performance Showdown: Efficiency, Purity, and Responsiveness
1. Efficiency and Performance Metrics
- PEM Electrolyzers:
- Efficiency: Typically 60-70% (HHV), with rapid advancements pushing higher.
- Dynamic Response: Exceptional, with start-up times in seconds and rapid load following capabilities. Ideal for renewable energy integration.
- Hydrogen Purity: Very high, 99.99% to 99.999%.
- Alkaline Electrolyzers:
- Efficiency: Similar range to PEM (50-65% HHV), but often operates at lower current densities.
- Dynamic Response: Slower, typically taking minutes to hours for full ramp-up/down. Less suited for highly fluctuating power.
- Hydrogen Purity: Good, 99.5-99.8%, but may require additional purification for sensitive applications.
PEM Alkalysis
| Feature | PEM Electrolysis | Alkaline Electrolysis |
|---|---|---|
| Electrolyte Type | Solid polymer (Nafion) | Liquid (KOH/NaOH) |
| Membrane/Separator | Yes, Solid barrier | No, Diaphragm/Separator |
| Operating Temperature | 50-80°C | 70-100°C |
| Operating Pressure | 30-70 bar (High) | 10-30 bar (Medium) |
| Current Density | 1-3 A/cm² (High) | 0.2-0.4 A/cm² (Low) |
| Dynamic Response | Milliseconds to seconds (Excellent) | Minutes to hours (Slow) |
| Hydrogen Purity | 99.99% – 99.999% (Ultra-High) | 99.5% – 99.8% (Good) |
| Capital Cost (relative) | Higher (due to PGMs) | Lower (non-PGM catalysts) |
| Material Cost (catalysts) | Platinum, Iridium (PGMs) | Nickel-based (Low Cost) |
| Typical Applications | Renewables Integration, Fueling Stations, Mobility, P2X, Electronics | Large-Scale Industrial H₂, Static/Base-Load Power, Chemical Plants |

Image 4: PEM vs. Alkaline Electrolysis: Making the Right Choice (Caption: A comparative overview highlighting the key differences between PEM electrolysis and traditional alkaline electrolysis. While alkaline systems offer lower initial CAPEX and utilize cheaper catalysts, PEM technology excels in dynamic responsiveness, higher hydrogen purity, and suitability for renewable energy integration. This table assists in matching the ideal electrolysis system to specific project requirements. Courtesy of Hele Titanium Hydrogen.)
C. Economic Considerations: CAPEX vs. OPEX and LCOH Implications
- Alkaline Electrolyzers: Generally have a lower initial CAPEX due to the use of more abundant and cheaper nickel-based catalysts, making them attractive for projects with stable, low-cost electricity supply and less stringent purity demands.
- PEM Electrolyzers: While having a higher CAPEX due to PGMs, their superior efficiency, dynamic response, and lower downstream purification needs can lead to a more competitive LCOH when integrated with renewable energy and demanding applications. The ability to utilize cheaper, intermittent renewable power effectively offsets the higher initial cost over the system’s lifetime.
D. Strategic Selection: Matching Technology to Your Project Needs
- Choose PEM if: Your project involves renewable energy sources (solar, wind), requires ultra-high purity hydrogen (e.g., fuel cells, electronics), demands rapid load changes, or has limited installation space.
- Choose Alkaline if: Your project has a stable, continuous power supply, requires large-scale industrial hydrogen production, has lower hydrogen purity requirements, and initial CAPEX is a dominant constraint.
Call to Action: Still unsure which electrolysis technology is best for your unique project? Our experts at Hele Titanium Hydrogen can provide a detailed consultation and recommend the optimal hydrogen production technology tailored to your operational and financial goals. Request a consultation today!
VII. Selecting the Right PEM Electrolysis System & Finding Your OEM Partner
Choosing the right PEM electrolysis system is a strategic decision that impacts the long-term viability and profitability of your green hydrogen initiatives. Partnering with a reliable OEM hydrogen generator manufacturer is equally crucial.
A. Critical Factors for System Evaluation
When assessing potential PEM electrolysis systems, consider these essential factors:
1. Required Hydrogen Purity & Production Capacity
- Purity: What are the exact purity requirements for your end application (e.g., 99.99% for industrial processes, 99.999% for fuel cells/electronics)? Ensure the system can consistently deliver this.
- Capacity: What is your projected hydrogen production demand (Nm³/hr or kg/day)? Ensure the system is scalable to meet current and future needs.
2. Power Source Characteristics
- Is your power source stable grid electricity or variable renewable energy (solar, wind)? PEM systems excel with renewables due to their dynamic response.
- What are the voltage and frequency requirements for the rectifier?
3. System Footprint and Scalability
- How much physical space is available for the electrolyzer stack and Balance of Plant (BOP)? PEM technology’s compact design is a significant advantage here.
- Can the system be easily expanded (e.g., by adding more modules) if production demand increases in the future?
4. Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
- Look beyond initial CAPEX. Analyze the Levelized Cost of Hydrogen (LCOH) over the system’s lifetime, factoring in OPEX (especially electricity), maintenance, and expected lifespan.
- Consider potential government incentives or carbon credits that can reduce TCO.
5. Safety Features and Certifications
- Verify adherence to international safety standards (e.g., ISO, CE, ATEX) for hydrogen handling and industrial equipment.
- Inquire about integrated safety systems, leak detection, and emergency shutdown protocols. This builds Trustworthiness.
6. After-Sales Support, Warranty, and Maintenance Contracts
- A robust warranty and readily available spare parts are crucial for minimizing downtime.
- Assess the supplier’s technical support capabilities, training programs, and maintenance service offerings.
B. The Value of Partnering with an Expert OEM & Manufacturer (Hele Titanium Hydrogen)
Choosing the right manufacturing partner is as important as selecting the right technology. An experienced OEM hydrogen generator supplier like Hele Titanium Hydrogen offers distinct advantages:
1. Customization and Design Flexibility
- We understand that every industrial application is unique. Hele Titanium Hydrogen excels in delivering bespoke PEM electrolysis systems tailored to your precise specifications, including specific output pressures, integration with existing infrastructure, and environmental conditions. Our Experience in diverse projects ensures optimal integration.
2. Quality Assurance and Reliability
- Our commitment to uncompromising quality is paramount.
Hele Titanium Hydrogen employs stringent manufacturing standards, meticulously sources premium materials (e.g., high-grade titanium for bipolar plates, carefully vetted membranes), and conducts rigorous testing protocols for every PEM water hydrogen generator before shipment. This robust quality control underscores our Trustworthiness and ensures exceptional system reliability.
3. Cost-Effectiveness through Optimized Production
- As a professional wholesale supplier and OEM hydrogen generator manufacturer, Hele Titanium Hydrogen leverages efficient production processes and economies of scale. This allows us to offer competitively priced, high-performance PEM electrolysis systems without compromising on quality or features, delivering excellent value to our B2B clients.
4. Technical Support and Expertise
- Our dedicated team of engineers possesses deep Expertise in PEM technology, electrochemistry, and system integration. We provide comprehensive technical support from initial design consultation through installation, commissioning, and ongoing operation, ensuring seamless project execution for our international clients.
5. Global Logistics and Supply Chain Efficiency
- With extensive experience in foreign trade, Hele Titanium Hydrogen manages efficient global logistics and supply chain operations, ensuring timely and reliable delivery of your PEM electrolysis systems to any destination worldwide.
C. Questions to Ask Potential PEM System Suppliers
To thoroughly vet potential vendors, go beyond basic inquiries:
- “What is your typical degradation rate for electrolyzer stacks under continuous operation, and how is it guaranteed?”
- “Can you provide references or case studies for installations similar to my required capacity and application?”
- “What level of automation and remote monitoring capabilities does your system offer?”
- “How easily can your PEM electrolysis systems integrate with various renewable energy sources and grid management systems?”
- “What are the specific details of your after-sales service, including response times and spare parts availability?”
- “What certifications (e.g., ISO 9001, CE, TUV) do your manufacturing processes and products hold?”
Hele’s Answer: At Hele Titanium Hydrogen, we welcome these detailed inquiries. Our transparent approach, proven track record, and comprehensive documentation ensure you have all the information needed to make a confident decision.
We pride ourselves on providing precise answers backed by data and our extensive Experience.
VIII. Future Trends & Innovations in PEM Technology
The field of PEM electrolysis is dynamic, with continuous innovation promising even greater efficiencies and cost reductions, further cementing its role in the green hydrogen economy.
A. Catalyst & Membrane Breakthroughs: Driving Down Costs & Boosting Performance
1. Reduced PGM Loading & Alternative Catalysts
Intensive research is focused on minimizing the reliance on expensive platinum group metals (PGMs). This includes:
- Lowering PGM Content: Developing highly active catalysts that require significantly less platinum or iridium per unit of hydrogen produced.
- Non-PGM Catalysts: Exploring earth-abundant materials (e.g., nickel, iron, cobalt-based alloys) as cost-effective alternatives, particularly for the oxygen evolution reaction at the anode. This is a key area for future cost of hydrogen reduction.
2. Enhanced Membrane Materials
Next-generation membranes are being developed to improve:
- Durability and Lifespan: Membranes that can withstand harsher operating conditions (higher temperatures, wider pH ranges) for longer periods.
- Ion Conductivity: Materials allowing faster proton transport, leading to lower energy losses.
- Cost Reduction: Developing less expensive membrane materials and manufacturing processes.
B. Advanced System Integration and Smart Controls
1. AI & Machine Learning for Predictive Maintenance and Optimization
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are being integrated to:
- Predictive Maintenance: Analyze operational data to anticipate component failures, enabling proactive maintenance and minimizing downtime.
- Performance Optimization: Dynamically adjust operating parameters (temperature, pressure, current) in real-time to maximize efficiency and hydrogen output based on electricity prices and demand.
2. Digital Twin Technology
Creating virtual replicas of physical PEM electrolysis systems allows for:
- Real-time Monitoring: Comprehensive oversight of system health and performance.
- Simulation and Scenario Planning: Testing operational strategies and predicting behavior without impacting the physical plant.
3. Integration with Renewable Energy Management Systems (REMS)
Seamless communication between PEM electrolyzers and REMS ensures optimized utilization of variable renewable energy sources, enhancing the overall efficiency of green hydrogen production facilities.
C. Scaling Up: The Path to Gigawatt-Scale PEM Plants
The hydrogen industry is rapidly moving towards larger scales. Major players and governments are planning gigawatt-scale PEM electrolysis plants to meet future demand. Challenges include manufacturing capacity, supply chain robustness, and efficient integration into large-scale energy infrastructure. However, the modular nature of PEM technology makes it well-suited for such ambitious expansion.
D. Global Policy & Market Dynamics Fueling PEM Growth
- Supportive Policies: Governments worldwide are implementing hydrogen strategies, offering significant financial incentives (e.g., tax credits, subsidies, grants) and establishing regulatory frameworks that favor green hydrogen and PEM electrolysis.
- Increasing Investment: Private and public investment in R&D and deployment of PEM systems continues to surge, reflecting confidence in the technology’s future.
- Growing Demand: Sectoral coupling (e.g., linking power, industry, and transport via hydrogen) continues to expand the market for PEM hydrogen production.
IX. Environmental & Sustainability Impact: PEM as a Climate Solution
The true value of PEM electrolysis lies in its profound environmental benefits and its role as a cornerstone of global sustainability efforts.
A. Quantifying Carbon Footprint Reduction
- By replacing hydrogen produced from steam methane reforming (SMR), which generates significant CO₂ emissions, with green hydrogen from PEM electrolysis, industries can drastically reduce their carbon footprint.
- Example: Producing 1 kg of hydrogen via SMR typically releases 9-10 kg of CO₂. A PEM electrolyzer powered by truly renewable energy produces virtually zero scope 1 and 2 carbon emissions at the point of production. Over the lifetime of a large-scale project, this translates to millions of tons of CO₂ avoided.
B. Contribution to Circular Economy
- Modern PEM electrolysis systems are designed with sustainability in mind, focusing on minimizing waste and maximizing resource efficiency.
- Research is ongoing into recycling precious metals from end-of-life electrolyzer components, moving towards a more circular economy for hydrogen production technology.
C. PEM’s Central Role in the Global Energy Transition and Achieving Net-Zero
PEM electrolysis is not just an incremental improvement; it is a transformative technology essential for achieving ambitious net-zero emission targets. It provides the clean hydrogen necessary to decarbonize:
- Heavy industry (steel, chemicals, cement).
- Long-haul transportation (shipping, aviation, heavy-duty road transport).
- Long-duration energy storage.
D. Safety and Environmental Considerations in Operations
While hydrogen is a flammable gas, modern PEM electrolysis systems are designed with multiple layers of safety:
- Robust Design: Adherence to international safety standards (e.g., ISO, IEC).
- Advanced Sensors & Controls: Continuous monitoring for hydrogen leaks and safe shutdown protocols.
- Ventilation: Proper site design ensures adequate ventilation to prevent hydrogen accumulation.
- Environmental Impact Assessments: Thorough assessments ensure minimal local environmental impact (e.g., water source management, noise).
Our Experience at Hele Titanium Hydrogen in designing and manufacturing safe PEM hydrogen generators is integrated into every product, adhering to stringent international safety standards to provide reliable and secure solutions.

X. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for PEM Electrolysis Buyers
Navigating the complexities of hydrogen production technology can raise many questions. Here are answers to some common inquiries from B2B buyers:
A. What makes PEM electrolysis superior for renewable energy integration?
PEM electrolysis systems offer exceptional dynamic response, allowing them to rapidly ramp up or down their hydrogen production in seconds to minutes. This enables them to efficiently utilize the intermittent and fluctuating power output from renewable energy sources like solar and wind, maximizing energy capture and mitigating curtailment.
B. What are the typical purity levels of hydrogen produced by PEM systems?
PEM electrolyzers inherently produce hydrogen of very high purity, typically ranging from 99.99% to 99.999%. This eliminates or significantly reduces the need for expensive downstream purification, making it ideal for high-spec applications such as fuel cells and electronics manufacturing.
C. How does the cost of PEM hydrogen compare to traditional grey hydrogen?
Currently, the Levelized Cost of Hydrogen (LCOH) for green hydrogen from PEM electrolysis is generally higher than that of grey hydrogen (from natural gas). However, due to rapidly falling renewable energy costs, decreasing
electrolyzer CAPEX, and technological advancements, PEM hydrogen is projected to achieve cost parity with, and eventually become cheaper than, grey hydrogen by 2030-2035 in many regions.
D. What are the main maintenance requirements and expected lifespan of a PEM electrolyzer stack?
PEM electrolysis systems are designed for relatively low maintenance due to their solid-state components. Routine checks, filter replacements, and periodic system diagnostics are typically required. The electrolyzer stack, which includes the membrane and catalysts, has an expected lifespan of 60,000 to 80,000 operating hours (equivalent to 7-9 years of continuous operation), with ongoing R&D aiming for 100,000+ hours.
E. Can PEM electrolyzers operate continuously, or are they best for intermittent use?
While PEM electrolyzers excel in intermittent operation for renewable energy integration due to their dynamic response, they are also highly capable of continuous, 24/7 operation. Their robust design ensures stable performance whether operating dynamically or at a steady state, making them versatile for various industrial hydrogen generation needs.
F. What are the safety considerations when installing and operating a PEM hydrogen production facility?
Safety is paramount. PEM hydrogen production facilities are designed with multiple safety features, including automated leak detection, ventilation systems, emergency shutdown protocols, and adherence to international safety standards (e.g., ISO, NFPA, ATEX).
Proper site planning, personnel training, and ongoing monitoring are crucial for safe operation.
G. How can Hele Titanium Hydrogen assist with custom PEM system design and manufacturing?
Hele Titanium Hydrogen specializes in OEM & Manufacturing services for PEM water hydrogen generators. We work closely with clients to understand their specific requirements (capacity, purity, pressure, integration needs) and leverage our Expertise to design, develop, and manufacture tailored PEM electrolysis systems that meet their exact operational and project specifications. Our Experience in custom solutions ensures optimal performance and seamless integration.
H. What are the space requirements for a typical industrial PEM electrolysis plant?
Thanks to their high current density, PEM electrolysis systems have a relatively compact footprint compared to older technologies. While the exact space depends on hydrogen production capacity and the configuration of the Balance of Plant (BOP), their modular design allows for efficient use of space and flexible layout options, making them suitable for sites with limited area.

XI. Conclusion: Powering the Future with Hele Titanium Hydrogen’s PEM Solutions
The transition to a sustainable, decarbonized future hinges on reliable, efficient, and scalable hydrogen production technology. Proton exchange membrane electrolysis systems stand out as the definitive next-generation solution, offering unparalleled efficiency, dynamic responsiveness for renewable energy integration, and the capability to produce ultra-high-purity green hydrogen. From decarbonizing heavy industry and enabling advanced energy storage to fueling sustainable mobility, PEM technology is pivotal.
While challenges related to CAPEX and PGM catalysts exist, relentless innovation, coupled with rapidly falling renewable energy prices and robust policy support, is swiftly driving down the Levelized Cost of Hydrogen (LCOH). PEM electrolysis is no longer just a promise; it is a commercially viable and strategically essential component of the emerging hydrogen economy.
At Hele Titanium Hydrogen, we are at the forefront of this revolution. With our deep Experience, specialized Expertise in PEM water hydrogen generators, rigorous manufacturing standards, and unwavering commitment to Trustworthiness, we are your ideal OEM & Manufacturing partner. We empower businesses worldwide to embrace green hydrogen by providing high-performance, custom-engineered PEM electrolysis systems that deliver exceptional value and reliability.
Don’t just adapt to the future—lead it with Hele Titanium Hydrogen.
Ready to unlock the potential of green hydrogen for your business?
Explore how Hele Titanium Hydrogen’s advanced PEM water hydrogen generators and comprehensive OEM & Manufacturing services can transform your operations.
- Browse our Products to see our range of high-performance PEM water hydrogen generators.
- Learn more about our OEM & Manufacturing Services and how we can support your specific needs, from custom design to large-scale production.
- Contact Us Today to discuss your project requirements and receive a personalized consultation. Let’s build your green hydrogen future together.
- Explore our FAQ for more insights into PEM technology and our offerings.
- Visit our Blog for the latest industry updates, technical deep dives, and market trends in hydrogen production technology.
Email Us: heletitaniumhydrogen@gmail.com
Phone/WhatsApp: 086-13857402537







