Introduction to HHO Generators:
An HHO generator is a device that produces a mixture of hydrogen and oxygen gas—commonly known as Brown’s gas—through the process of water electrolysis. This DIY HHO generator guide is designed to help you safely and efficiently build your own hydrogen generator at home, whether your goal is to experiment with alternative fuels, enhance fuel efficiency, or explore the science of water electrolysis.
The principle behind an HHO generator revolves around the electrolysis of water. By passing an electric current through water containing an electrolyte, water molecules (H2O) are split into hydrogen (H2) and oxygen (O2) gases. The resulting HHO gas can be used for various applications, such as welding, supplementing fuel in combustion engines, and even laboratory experiments.
Before embarking on your homemade hydrogen project, it’s crucial to understand the inherent risks. Hydrogen is highly flammable, and improper handling can lead to dangerous situations. Proper safety measures, ventilation, and secure build practices are essential components of any successful and safe HHO generator project.

Materials and Tools Needed:
Building a reliable DIY HHO generator requires specific materials and tools, each chosen for optimal safety and efficiency.
- Core Components:
- Stainless steel plates (preferably 316L grade for corrosion resistance and durability)
- Electrolyte solution, such as potassium hydroxide (KOH) or sodium hydroxide (NaOH), to increase water conductivity
- High-quality power supply (capable of providing stable DC current, typically 12V–24V)
- Gas collection system, including tubing and a reservoir for capturing and storing the generated gas
- Sealed container that can withstand internal pressure and prevent leaks
- Essential Tools:
- Multimeter for monitoring voltage and current throughout operation
- Soldering iron for secure electrical connections
- Safety equipment, including goggles, chemical-resistant gloves, and a fire extinguisher
Gathering these materials and tools before starting ensures a smooth assembly process and helps mitigate safety risks.
Step-by-Step Assembly Guide:
Constructing your own hydrogen generator involves careful preparation and attention to detail at each stage. Follow these sequential steps for optimal results:
Step 1: Preparing the Electrolysis Plates
Begin by cutting stainless steel plates to uniform size and cleaning them thoroughly to remove any oils or contaminants. The spacing between plates is crucial; a gap of 1–3 mm typically offers a balance between efficient gas production and electrical resistance. Decide on a plate configuration—either series or parallel. Series connections are generally favored, as they allow for more efficient voltage distribution across each cell, resulting in improved gas output.
Step 2: Building the Electrolysis Chamber
Select a sturdy, non-reactive container (such as high-density polyethylene or glass) that can be sealed tightly. Modify the container to fit the plates securely, ensuring they are suspended without touching one another. Install water level indicators to monitor the electrolyte solution during operation, which helps prevent dry-out or overflow.
Step 3: Electrical Connections
Use insulated copper wiring to connect the plates according to your chosen configuration. Install a fuse rated slightly above your intended current draw to protect the circuit from overload. Add an accessible on/off switch for safe operation. Double-check all wiring for secure, corrosion-resistant connections, and use a multimeter to verify voltage and continuity before powering on.
Step 4: Gas Collection System
Attach gas-tight tubing to a collection port on the chamber lid. Route the tubing to a gas reservoir or bubbler. To prevent flashback—a dangerous situation where a flame travels back into the generator—install a flashback arrestor in the gas line. Efficient bubble management within the reservoir will help maximize gas purity and reduce water carryover.
Optimizing Your HHO Generator:
Maximizing the performance and longevity of your DIY HHO generator requires careful optimization.
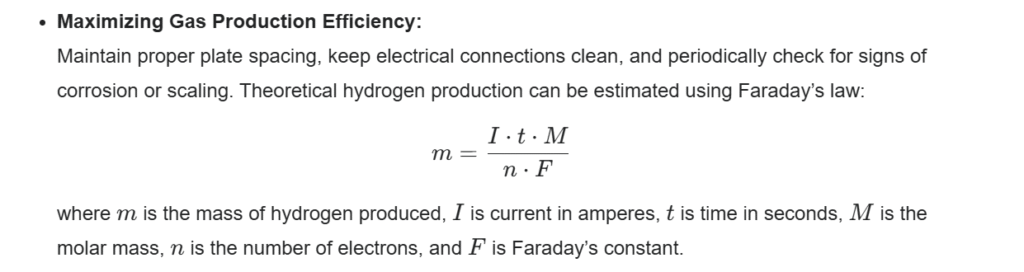
Maximizing Gas Production Efficiency:
Maintain proper plate spacing, keep electrical connections clean, and periodically check for signs of corrosion or scaling. Theoretical hydrogen production can be estimated using Faraday’s law.
- Electrolyte Concentration Ratios:
The concentration of KOH or NaOH in your electrolyte solution directly affects conductivity and gas production. A typical starting ratio is 4–6% by weight, but you should adjust this based on your current draw and desired output. - Temperature Management:
Electrolysis generates heat. Excessive temperatures can reduce efficiency and damage components. Monitor electrolyte temperature and, if necessary, use cooling fans or heat sinks to maintain safe levels (ideally below 60°C). - Troubleshooting Common Issues:
If gas output drops or the system overheats, check for dirty plates, inadequate electrolyte, or faulty electrical connections. Regular maintenance and monitoring help prevent these issues.
Safety Protocols and Best Practices:
Safety must be the top priority when working with hydrogen generators.
- Proper Ventilation Requirements:
Operate your DIY HHO generator in a well-ventilated area to prevent dangerous hydrogen buildup. Never use the device in enclosed or poorly ventilated spaces. - Fire Prevention Measures:
Keep ignition sources, open flames, and static discharge away from the generator and gas storage areas. Always have a fire extinguisher rated for chemical and electrical fires nearby. - Handling and Storage of Hydrogen Gas:
Only use approved, pressure-rated containers for storing hydrogen. Never store large quantities of HHO gas indoors, and avoid prolonged storage to reduce risk. - Maintenance Schedule:
Regularly inspect the generator for leaks, corrosion, and wear. Replace worn seals and damaged components promptly. Clean the plates and change the electrolyte solution as needed to maintain optimal performance.
Industrial-Grade HHO Solutions for Businesses:
While a DIY HHO generator is ideal for home experimentation and small-scale applications, it has significant limitations for commercial use.
- Limitations of DIY Systems:
Homemade hydrogen generators usually lack the capacity, safety certifications, and automation required for industrial applications. They are best suited for learning and low-volume tasks. - Professional HHO Generators for Industrial Applications:
Commercial hydrogen generators feature robust safety systems, automated controls, and scalable gas output. These systems are designed for continuous operation and compliance with industry standards. - Key Features of Commercial-Grade Systems:
Professional units often include integrated flashback arrestors, automated monitoring, remote diagnostics, and advanced cooling systems. They also provide detailed operational data for process optimization. - Cost-Benefit Analysis for Business Implementation:
Investing in a commercial hydrogen generator can offer long-term savings, higher productivity, and greater safety. Although the upfront cost is higher than a DIY build, the reliability and efficiency benefits make it a sound choice for businesses seeking sustainable energy or fuel solutions.
Conclusion:
Building a DIY HHO generator offers a fascinating introduction to the science of hydrogen production and practical experience with water electrolysis. With the right materials, careful assembly, and a strong focus on safety, you can create a reliable hydrogen generator for home or hobby use. However, for larger-scale or business-critical applications, investing in a professionally engineered system is the best course.
Ready to take your hydrogen technology to the next level?
Contact our hydrogen technology experts to explore commercial-grade HHO solutions tailored to your business. Request a consultation today to discuss your requirements and receive a customized quote—empowering your operation with safe, efficient hydrogen production.







