Introduction
In the quest for sustainable energy solutions, alkaline electrolysis of water has emerged as a pivotal technology for hydrogen production. This process not only contributes to reducing carbon emissions but also plays a crucial role in the burgeoning hydrogen economy. This article delves into the mechanics of alkaline electrolysis, its advantages over other methods, and its potential impact on future energy systems.
Understanding Alkaline Electrolysis
What is Alkaline Electrolysis?
Alkaline electrolysis is a method that uses an electrolyzer to split water (H₂O) into hydrogen (H₂) and oxygen (O₂) gases through an electrochemical reaction. This process occurs in an alkaline solution, typically potassium hydroxide (KOH), which facilitates ion transport between two electrodes—an anode and a cathode—immersed in the electrolyte solution[1][7].
The Electrolysis Process
The electrolysis process can be summarized in two main reactions:
- At the Cathode: Water molecules are reduced, producing hydrogen gas and hydroxide ions:
$$ 2H_2O + 2e^- \rightarrow H_2 + 2OH^- $$
- At the Anode: Hydroxide ions are oxidized to produce oxygen gas and water:
$$ 2OH^- \rightarrow \frac{1}{2}O_2 + H_2O + 2e^- $$
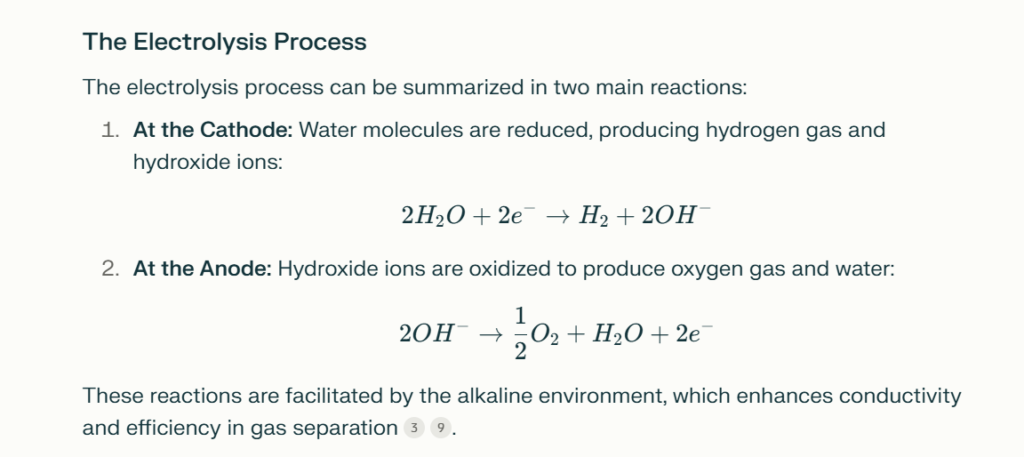
These reactions are facilitated by the alkaline environment, which enhances conductivity and efficiency in gas separation[3][9].
Advantages of Alkaline Electrolysis
Cost-Effectiveness
One of the primary benefits of alkaline electrolysis is its cost-effectiveness. The materials used in alkaline electrolyzers, such as nickel-based catalysts, are generally less expensive than those used in proton exchange membrane (PEM) electrolyzers, which often require precious metals like platinum[7]. This makes alkaline systems more accessible for large-scale hydrogen production.
Scalability
Alkaline electrolyzers can be easily scaled to meet varying demands. They can operate efficiently at megawatt-scale capacities, making them suitable for both small and large hydrogen production facilities[6][8]. This flexibility allows industries to adjust their hydrogen output based on market needs.
High Purity Hydrogen Production
The design of alkaline electrolyzers ensures that hydrogen and oxygen gases are effectively separated during the electrolysis process. This results in high-purity hydrogen, which is essential for applications such as fuel cells and industrial processes[7][9]. The purity level achieved through alkaline electrolysis often exceeds that of other methods.
Applications of Hydrogen Produced from Alkaline Electrolysis
Hydrogen produced via alkaline electrolysis has a wide range of applications:
- Fuel Cell Vehicles: Hydrogen serves as a clean fuel alternative for vehicles powered by fuel cells, contributing to reduced greenhouse gas emissions.
- Industrial Processes: Industries utilize hydrogen for various chemical processes, including ammonia synthesis and petroleum refining.
- Energy Storage: Hydrogen can be stored and converted back into electricity when needed, providing a solution for intermittent renewable energy sources like wind and solar power.
- Power Generation: Hydrogen can be burned directly in turbines or used in fuel cells to generate electricity without harmful emissions[6].
Challenges Facing Alkaline Electrolysis
Despite its advantages, alkaline electrolysis faces several challenges:
Efficiency Concerns
While alkaline electrolysis is generally efficient, it may not match the performance levels of PEM electrolyzers under certain conditions. Research is ongoing to enhance the efficiency of alkaline systems through improved catalysts and cell designs[9].
Durability and Maintenance
The longevity of alkaline electrolyzers can be affected by factors such as corrosion and electrode degradation over time. Regular maintenance is essential to ensure optimal performance and extend the lifespan of these systems[6][8].
Future Prospects
The future of alkaline electrolysis appears promising as global demand for clean hydrogen continues to rise. Ongoing research aims to improve efficiency, reduce costs further, and develop more durable materials that can withstand harsh operating conditions[6]. Furthermore, as governments worldwide implement policies favoring renewable energy technologies, alkaline electrolysis stands poised to play a significant role in achieving sustainability goals.
Conclusion
Alkaline electrolysis of water represents a vital technology in the transition towards sustainable energy solutions. By producing high-purity hydrogen efficiently and cost-effectively, it supports various applications that contribute to reducing carbon footprints across multiple sectors. As advancements continue in this field, the potential for alkaline electrolysis to reshape our energy landscape becomes increasingly evident.
This comprehensive overview not only highlights the significance of alkaline electrolysis but also positions it as a key player in the future of hydrogen production and sustainable energy technologies.
Hele Titanium Hydrogen: Your Trusted PEM electrolyzer OEM & Manufacturing Partner
Hele Titanium Hydrogen stands as a reliable and experienced partner in the PEM electrolyzer OEM supply chain. We specialize in the design, development, and manufacturing of high-performance PEM Water Hydrogen PEM electrolysis system, offering comprehensive OEM & Manufacturing services tailored to your specific needs.
Take the Next Step
Ready to explore the possibilities of partnering with Hele Titanium Hydrogen?
- Browse our Products to see our range of PEM Water Hydrogen production equipment.
- Learn more about our Services and how we can support your OEM & Manufacturing needs.
- Contact Us today to discuss your specific requirements.
- Explore our FAQ to get answers to common questions.
- Visit our Blog for the latest insights and updates on hydrogen technology.
Email Us: heletitaniumhydrogen@gmail.com
Phone/WhatsApp: 086-13857402537
Citations:
[1] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alkaline_water_electrolysis
[2] https://www.copy.ai/tools/meta-description-generator
[3] https://www.new-era-insights.com/article/the-four-main-types-of-water-electrolysis-technology/
[4] https://help.hypotenuse.ai/article/133-bulk-meta-titles-and-descriptions
[6] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Z05KmkxBBUw
[7] https://www.ineos.com/businesses/ineos-electrochemical-solutions/electrolysers/alkaline-water-electrolysers/
[8] https://writesonic.com/blog/seo-meta-tags
[9] https://www.scielo.br/j/qn/a/KyQvF9DMHK6ZJXyL5zQNy7N







