Introduction to Hydrogen Electrolysis
In the contemporary landscape of energy production, hydrogen electrolysis has emerged as a critical technology for generating clean and sustainable energy. This process involves splitting water (H₂O) into its constituent elements—hydrogen (H₂) and oxygen (O₂)—using an electric current. As industries worldwide strive to reduce their carbon emissions and transition to renewable energy sources, hydrogen electrolysis plays a pivotal role in this transformation.
Understanding the Process of Hydrogen Electrolysis
Hydrogen electrolysis occurs in an electrolyzer, which consists of two electrodes (anode and cathode) separated by an electrolyte. When an electric current is applied, water molecules are dissociated into hydrogen and oxygen gases. The overall reaction can be summarized as follows:
$$ 2H_2O(l) \rightarrow 2H_2(g) + O_2(g) $$
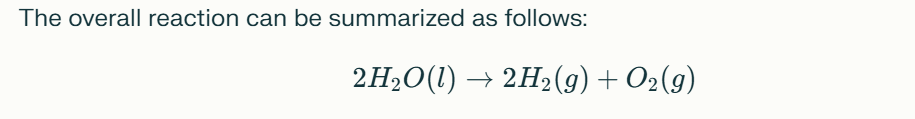
This equation illustrates the fundamental principle of electrolysis, where water is transformed into hydrogen and oxygen through the application of electrical energy.
The Importance of Hydrogen in the Energy Transition
Hydrogen is increasingly recognized as a versatile energy carrier that can significantly contribute to decarbonizing various sectors. Its applications span from industrial processes to transportation and energy storage. Here are some key areas where hydrogen plays a crucial role:
1. Industrial Applications
Hydrogen is utilized in several industrial processes, including:
- Ammonia Production: Used as a feedstock for fertilizers.
- Oil Refining: Essential for hydrocracking and desulfurization processes.
- Steel Manufacturing: Hydrogen is being explored as a cleaner alternative to coal in steel production, potentially reducing carbon emissions significantly.
2. Transportation Sector
The transportation industry is undergoing a significant transformation with the adoption of hydrogen fuel cells:
- Fuel Cell Vehicles (FCVs): Hydrogen fuel cells provide a clean alternative to conventional gasoline and diesel engines, emitting only water vapor as a byproduct.
- Heavy-Duty Transport: Hydrogen is being considered for use in trucks, buses, and trains, particularly for long-distance travel where battery solutions may be less viable.
3. Energy Storage Solutions
Hydrogen serves as an effective energy storage medium:
- Renewable Energy Integration: Excess electricity generated from renewable sources can be converted into hydrogen through electrolysis, providing a means to store energy for later use.
- Grid Stability: Hydrogen can help balance supply and demand on electricity grids by acting as a buffer during periods of high renewable generation.
Benefits of Hydrogen Electrolysis
1. Sustainability
Hydrogen produced via electrolysis can be classified as “green hydrogen” when generated using renewable energy sources such as wind or solar power. This process significantly reduces greenhouse gas emissions compared to conventional fossil fuel-based hydrogen production methods.
2. High Purity Output
Electrolysis produces high-purity hydrogen, essential for applications requiring clean fuel. The purity levels often exceed 99.9995%, making it suitable for sensitive industrial applications such as semiconductor manufacturing and fuel cells.
3. Scalability
Electrolyzer systems can be scaled up or down based on demand:
- Modular Design: Many modern electrolyzers are designed with modular components that allow for easy expansion as hydrogen needs grow.
- Adaptability: This scalability makes electrolyzers suitable for both small-scale applications (like residential use) and large industrial setups.
4. Reduced Dependency on Fossil Fuels
By utilizing renewable energy sources to produce hydrogen, industries can reduce their reliance on fossil fuels, contributing to energy independence and enhancing energy security.
Types of Electrolyzers
There are several types of electrolyzers used in hydrogen production, each with its own advantages:
1. Alkaline Electrolyzers
Alkaline electrolyzers have been the traditional choice for hydrogen production:
- Cost-Effective: Generally lower capital costs compared to other technologies.
- Mature Technology: Well-established with a proven track record in various industrial applications.
2. Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM) Electrolyzers
PEM electrolyzers are gaining popularity due to their efficiency and versatility:
- Higher Efficiency: Typically operate at higher efficiencies than alkaline systems.
- Compact Design: Smaller footprint makes them suitable for various applications, including portable setups.
3. Solid Oxide Electrolyzers (SOE)
SOE technology is emerging as a promising option:
- High Efficiency: Capable of achieving higher efficiencies than both alkaline and PEM technologies.
- Utilization of Waste Heat: Can leverage waste heat from industrial processes or concentrated solar power.
Applications of Hydrogen Electrolysis
1. Energy Generation
Hydrogen electrolysis can be integrated into renewable energy systems to generate clean electricity:
- Power-to-Gas Systems: Excess renewable energy can be converted into hydrogen for storage or direct use in fuel cells.
2. Chemical Production
The chemical industry is increasingly adopting green hydrogen:
- Methanol Production: Utilizing green hydrogen in methanol synthesis helps reduce carbon emissions associated with traditional methods.
- Synthetic Fuels: Hydrogen can be combined with carbon dioxide to produce synthetic fuels, contributing to decarbonization efforts.
3. Water Treatment
Hydrogen electrolysis has applications in water treatment processes:
- Wastewater Treatment: Hydrogen can be used in advanced oxidation processes to treat contaminated water effectively.
Challenges Facing Hydrogen Electrolysis
While hydrogen electrolysis offers numerous benefits, there are challenges that need addressing:
1. High Initial Costs
The capital investment required for electrolyzer systems can be significant, which may deter some businesses from adopting this technology.
2. Energy Requirements
Electrolysis requires substantial electrical energy input, which needs to be sourced sustainably to maximize environmental benefits.
3. Infrastructure Development
The widespread adoption of hydrogen technology necessitates the development of infrastructure for production, storage, distribution, and utilization.
Conclusion
Hydrogen electrolysis stands at the forefront of the transition towards sustainable energy solutions. By producing green hydrogen from renewable sources, this technology not only addresses the pressing need for clean energy but also supports various industries in their decarbonization efforts.
As interest in hydrogen continues to grow globally, investing in advanced electrolyzer technology will be crucial for businesses looking to enhance their operational efficiency while contributing positively to environmental sustainability.
Call to Action
Are you interested in exploring how hydrogen electrolysis can transform your energy strategy? Contact us today to learn more about our innovative electrolyzer solutions tailored specifically for your needs! Together, we can drive the transition towards a cleaner and more sustainable future!