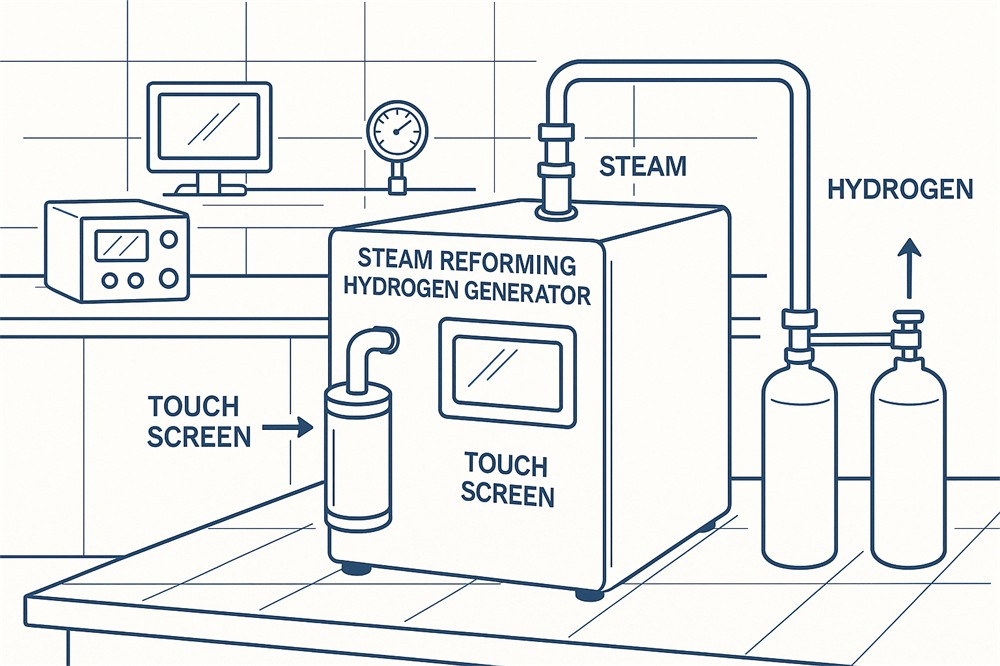
Understanding PEM Electrolysis Cells: The Future of Green Hydrogen Production
The global shift towards sustainable energy sources has heightened interest in hydrogen production technologies. At the forefront of this movement is the proton exchange membrane (PEM) electrolysis cell, a promising technology for producing green hydrogen. This article delves into the intricacies of PEM electrolysis cells, exploring their operation, advantages, and potential impact on the energy landscape.
What is a PEM Electrolysis Cell?
A PEM electrolysis cell is an advanced technology used to split water into hydrogen and oxygen using electricity. The core component of this system is the proton exchange membrane, a solid polymer that conducts protons while separating the product gases and providing electrical insulation for the electrodes. This technology stands out due to its ability to operate at high current densities and its compact, efficient design.
Key Features of PEM Electrolysis
- Solid Polymer Electrolyte: The PEM serves as both the electrolyte and the separator, eliminating the need for hazardous liquid electrolytes.
- High Purity Hydrogen Production: The solid structure of the membrane minimizes gas crossover, ensuring high purity hydrogen.
- Dynamic Response: PEM electrolysis systems can quickly adapt to changes in electricity supply, making them ideal for integration with renewable energy sources like wind and solar power.
Certainly! Here’s the text from the image in markdown format:
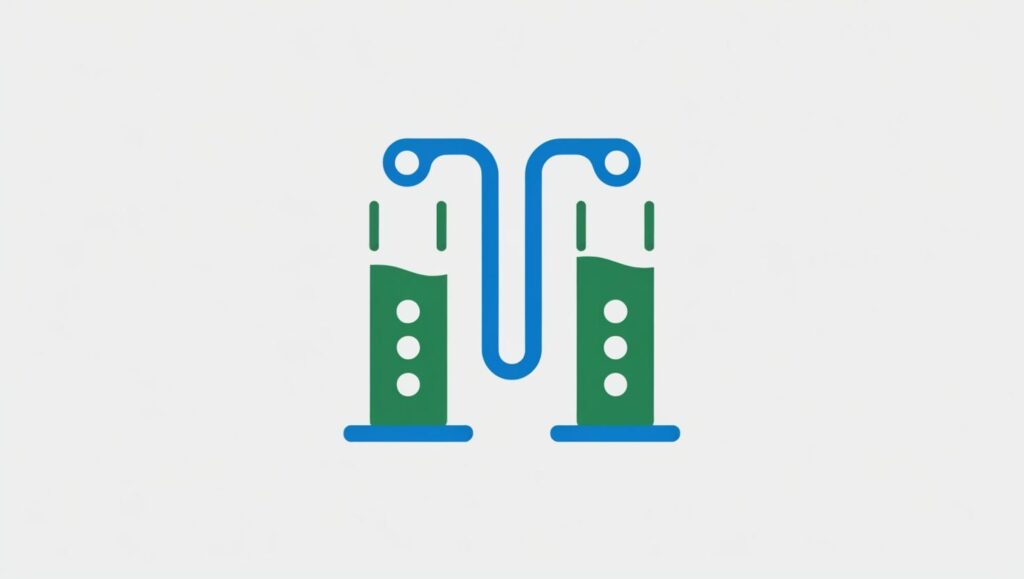

How Does PEM Electrolysis Work?
The PEM electrolysis process involves two main reactions:
- At the Anode (Oxygen Evolution Reaction – OER):
- Water molecules are oxidized to produce oxygen gas, protons, and electrons.
- At the Cathode (Hydrogen Evolution Reaction – HER):
Protons migrate through the PEM to the cathode, where they combine with electrons to form hydrogen gas.
Note: for details Reaction information as below:

The overall reaction is the electrolysis of water, where electrical energy is used to decompose water into hydrogen and oxygen gases.
Advantages of PEM Electrolysis
PEM electrolysis offers several benefits over traditional alkaline electrolysis:
- Higher Efficiency: PEM systems operate at higher current densities, reducing operational costs and improving energy efficiency.
- Compact Design: The use of a solid polymer membrane allows for a more compact and lightweight design, which is crucial for applications with space constraints.
- Rapid Start-Up: PEM electrolyzers can quickly start and adjust to varying loads, making them highly compatible with intermittent renewable energy sources.
- Environmental Impact: When powered by renewable energy, PEM electrolysis is a carbon-neutral process, producing only oxygen as a byproduct.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Despite its advantages, PEM electrolysis faces challenges that must be addressed to facilitate widespread adoption:
- Cost of Materials: The use of precious metals like platinum and iridium as catalysts increases the cost of PEM systems. Research is ongoing to find alternative materials that can reduce costs without compromising performance.
- Durability and Longevity: Ensuring the long-term stability and durability of PEM electrolyzers is crucial for their economic viability. Advances in materials science are needed to enhance the lifespan of these systems.
- Scalability: While PEM technology is well-suited for small to medium-scale applications, scaling up for industrial hydrogen production remains a challenge.
The Role of PEM Electrolysis in the Hydrogen Economy
PEM electrolysis is poised to play a pivotal role in the emerging hydrogen economy. By providing a method to produce green hydrogen, PEM technology can help decarbonize sectors that are difficult to electrify, such as heavy industry and long-haul transportation. The integration of PEM electrolyzers with renewable energy sources can also stabilize electrical grids by storing excess energy as hydrogen, which can be converted back to electricity or used as a fuel.
Conclusion
PEM electrolysis cells represent a significant advancement in hydrogen production technology, offering a sustainable and efficient method to generate green hydrogen. As research continues to address the challenges of cost and scalability, PEM technology is expected to become a cornerstone of the global transition to a clean energy future.
For those interested in exploring the potential of PEM electrolysis further, consider diving into the latest research on alternative catalyst materials or investigating how this technology can be integrated with renewable energy systems. By staying informed and engaged, you can be part of the movement towards a more sustainable and hydrogen-powered world.
PEM Electrolysis Cells Boosting Hydrogen Infrastructure Investment: A Sustainable Energy Solution Call to Action
As the world moves towards a sustainable energy future, understanding and supporting technologies like PEM electrolysis is crucial. Share this article with others interested in green energy solutions, and explore opportunities to advocate for investments in hydrogen infrastructure and research. Together, we can accelerate the transition to a cleaner, greener planet.