PEM Water Electrolyzers: Advancing Industrial and Renewable Hydrogen Production

In the quest for sustainable energy solutions, hydrogen has emerged as a promising alternative to fossil fuels. Central to this hydrogen revolution is the Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM) technology, which offers efficient and clean hydrogen production. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of PEM water electrolyzers, PEM hydrogen generators, and PEM electrolyzer stacks, exploring their functionality, benefits, and applications.
What is a PEM Water Electrolyzer?
A PEM water electrolyzer is a device that splits water into hydrogen and oxygen using electricity. The core technology involves a proton exchange membrane that facilitates the separation of hydrogen ions from oxygen ions. This process is not only efficient but also environmentally friendly, as it produces pure hydrogen without any carbon emissions.
Key Components of a PEM Water Electrolyzer
- Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM): The heart of the electrolyzer, usually made from Nafion, which allows protons to pass through while blocking gases like hydrogen and oxygen.
- Electrodes: Typically made of platinum and iridium oxide, these electrodes catalyze the water-splitting reaction.
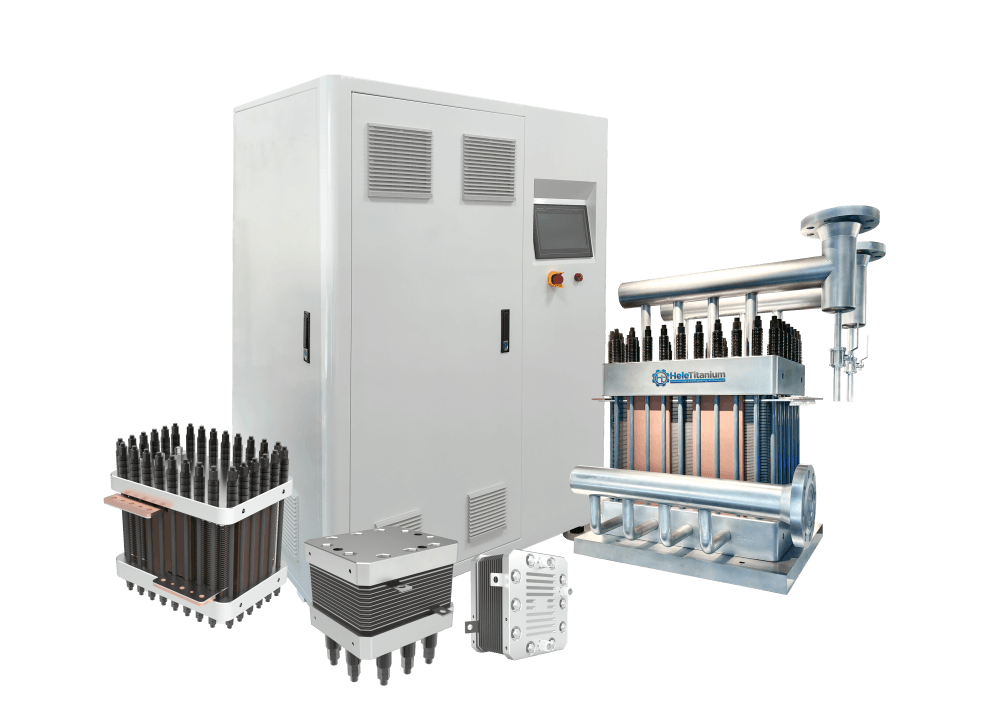
- Electrolyzer Stack: Composed of multiple cells, each containing a membrane and electrodes, the stack determines the electrolyzer’s capacity and efficiency.
How Does a PEM Hydrogen Generator Work?
The PEM hydrogen generator operates on the principle of electrolysis. When an electric current passes through the water, it splits into hydrogen and oxygen gases. The PEM facilitates the movement of protons from the anode to the cathode, where they combine with electrons to form hydrogen molecules. This hydrogen can then be stored or used immediately as a clean energy source.
Advantages of PEM Hydrogen Generators
- High Purity: Produces hydrogen with purity levels greater than 99.99%.
- Efficiency: Low overpotential and high current densities result in efficient hydrogen production.
- Scalability: Easily scalable from small laboratory setups to large industrial applications.
- Renewable Energy Integration: Can be powered by renewable energy sources like solar and wind, enhancing sustainability.
Exploring PEM Electrolyzer Stacks
A PEM electrolyzer stack is a series of cells connected in series or parallel to increase the hydrogen production capacity. The stack’s design and configuration significantly impact the overall performance and efficiency of the electrolyzer.
Types of PEM Electrolyzer Stacks
- Small Stack Configurations: Typically used for laboratory and research purposes, these stacks range from 1 to 24 cells.
- Large Stack Configurations: Designed for industrial applications, these stacks can reach up to 48 cells or more, offering higher hydrogen production rates.
Technical Specifications
- Operating Voltage and Current: Typically ranges from 1.7V to 2V per cell, with current densities up to 40 amps.
- Pressure and Temperature: Capable of generating pressures up to 10 bar and operating temperatures between 15°C to 70°C.
- Water Quality: Requires high-purity distilled water (16-18 megaohms) for optimal performance.
Applications of PEM Water Electrolyzers
PEM water electrolyzers have a wide array of applications across various industries, owing to their versatility and efficiency.
Key Applications
- Renewable Energy Storage: Hydrogen produced can be stored and converted back to electricity using fuel cells, providing a reliable energy storage solution.
- Industrial Hydrogen Supply: Used in industries requiring ultra-pure hydrogen, such as semiconductor manufacturing and chemical processing.
- Laboratory Research: Essential in research settings for experiments requiring high-purity hydrogen and oxygen gases.
- Hydrogen Fueling Stations: Integral to the infrastructure for hydrogen-powered vehicles, offering a sustainable fueling solution.
Challenges and Future Prospects
While PEM water electrolyzers offer numerous advantages, they also face certain challenges that need addressing for widespread adoption.
Challenges
- Cost: The use of precious metals like platinum and iridium in electrodes contributes to high production costs.
- Durability: The operational lifetime of PEM electrolyzers is influenced by factors such as water quality and operating conditions.
Future Developments
- Material Innovation: Research is ongoing to find cost-effective alternatives to precious metals, potentially reducing costs.
- System Integration: Advances in integrating PEM electrolyzers with renewable energy sources could enhance their viability as a sustainable energy solution.
Conclusion
PEM water electrolyzers represent a pivotal technology in the transition to a hydrogen-based economy. Their ability to produce clean, high-purity hydrogen efficiently makes them indispensable in both industrial and renewable energy applications. As advancements continue to address current challenges, PEM electrolyzers are poised to play a crucial role in achieving a sustainable energy future.
For those interested in exploring the potential of PEM technology further, consider investing in a PEM electrolyzer stack tailored to your specific needs. Whether for research, industrial applications, or renewable energy integration, PEM water electrolyzers offer a pathway to cleaner and more sustainable energy solutions.
By understanding the capabilities and applications of PEM water electrolyzers, stakeholders can make informed decisions to harness the power of hydrogen, paving the way for a greener and more sustainable world.